All About Strapping
Using strapping in your packaging line can help reinforce packages in different ways. In today’s post we are going to outline the most common uses, benefits, and drawbacks of different strapping materials to help you determine if your packaging configuration could benefit.
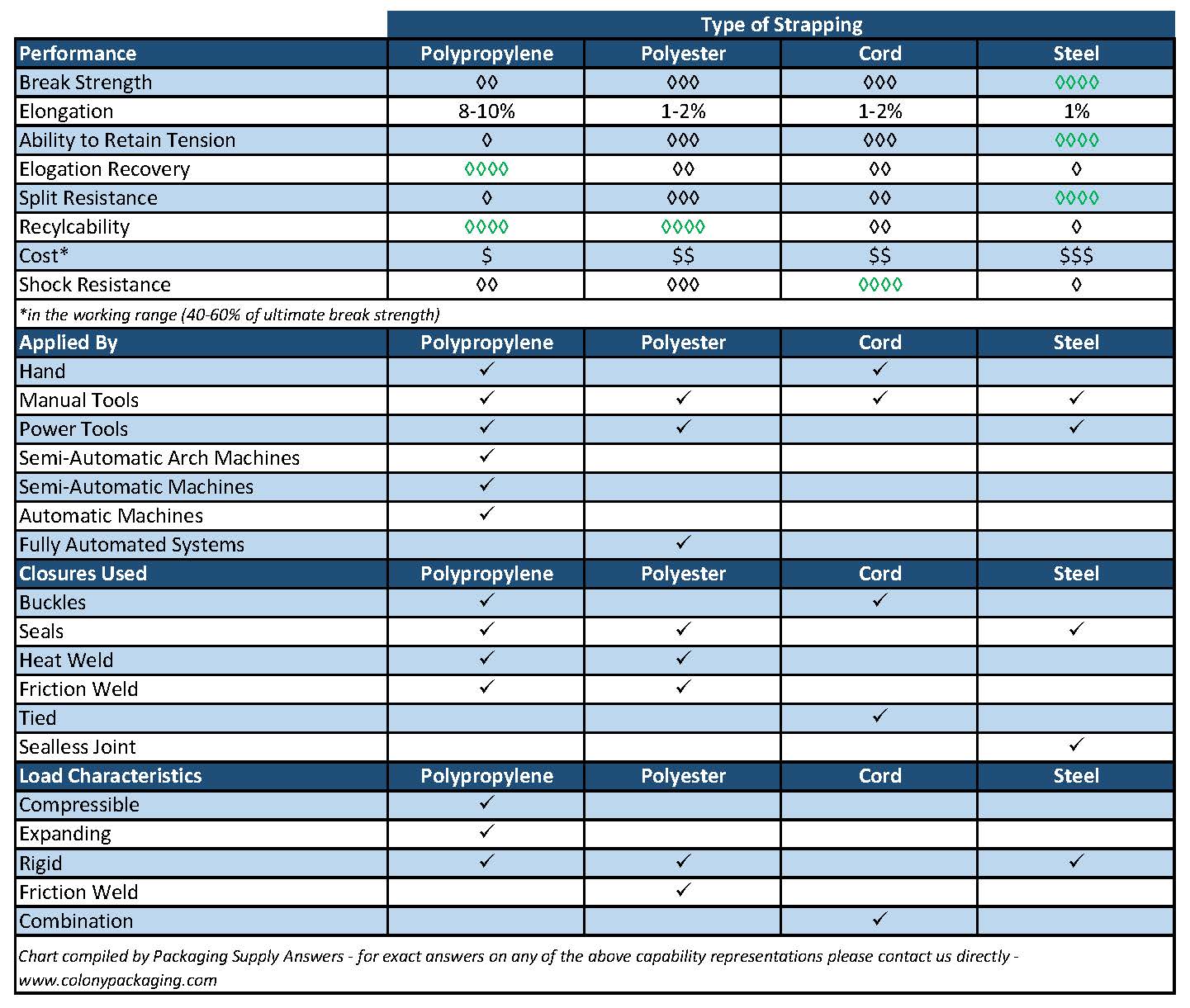
There are four different strapping mediums: steel, polyester (PET), polypropylene (polypro), and cording.
Steel Strapping
Steel strapping is the strongest of all the strapping materials. It is recommended where high strength is necessary, low elongation (stretch) is important, and where the product may be sharp or hot. Steel strapping is sealed using mechanical seals and notch (sealless) type joints. It is still the preferred alternative in many industries.
Advantages – High strength, low elongation
Disadvantages – Relatively expensive, sharp edges, difficult to recycle
Applications – Sharp or hot products, steel, rail car, heavy construction
Polypropylene Strapping
Polypropylene strapping is the most commonly used and least expensive of all strapping materials. It is light, easy to apply, and easy to recycle. Its primary characteristics are high elongation (stretch) and elongation recovery. It has, however, a low retained tension. Polypropylene strapping is available in hand grade and machine grade, and can be sealed with buckles, seals, heat seals, or friction welds. Worth noting, machine grade strapping can be used with manual tools, but hand grade strapping should not be used in a machine application. Polypropylene is used in all automatic strapping machines and almost all stand-alone arch strapping machines.
Advantages – Most cost effective, lightweight, easy to apply, easy to recycle, high elongation, high elongation recover
Disadvantages – Low retained tension, potential to split
Applications – Light duty palletizing, unitizing, carton closing, bundling
Polyester
Polyester (or PET) is the most rigid of the strapping options. It has significantly less elongation than polypropylene and retains tension over a longer period of time. Polyester strap is nick resistant and is sealed with seals, heat, or friction welds.
Since polyester strapping offers the highest strength and greatest retained tension of all the plastic strapping, it is often used on heavy duty loads that need high initial tension along with high retained tension during handling and storage. Additionally, competitive pricing and performance characteristics have motivated many steel strapping uses to switch to polyester. Polyester strapping is available in both machine grade and hand grade and is easy to dispose of and recycle.
Advantages – Most rigid, long tension retention, high strength, nick resistant, easy to recycle
Disadvantages – Less elongation than polypropylene
Applications – Empty cans and bottles, lumber, heavy/rigid pallet loads, steel replacement
Cord Strapping
Cord strapping is available in both polyester and rayon, and comes in two basic forms – uniline and cross woven. Cord is used only in manual applications and is sealed using buckles, seals, or is tied. Polyester cord offers excellent resistance to moisture and is frequently used in outdoor applications. Heavy duty polyester cord is frequently replacing steel in lumber applications.
Advantages – Can be manual applied with no tools, moisture resistant
Disadvantages – Poor elongation, difficult to recycle
Applications – Steel replacement, agricultural, boating
The chart below illustrates the advantages of each type of strapping and compares the relative performance of each. It also indicates what types of applications will work with that material. Definitions of these characteristics can be found below.
Is strapping the right product for you? Contact your sales representative for best options for your application and for more information regarding the machines and tools we have available.
